AWS Tutorial
Elastic Load Balancing
Author: Emad Zaamout
Sunday, October 18, 2021
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Single AWS EC2 Model Implications.
- What is AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)?
- How AWS Elastic Load Balancing Works?
- AWS Elastic Load Balancers Internet-facing vs Internal
- What is AWS EC2 Auto Scaling?
Introduction
Welcome back
In this tutorial, I am going to show you how to set up Load Balancers and Target Groups. First, we will create an EC2 instance to run our server. Then we will create a Target Group and a Load Balancer to route HTTP traffic.
If your completely new to Load Balancing, I highly recommend you watch our AWS Elastic Load Balancing Explained video, links in the description.
Single AWS EC2 Model Implications
Let’s begin with an example.
Suppose that you have single EC2 Instance running your application.
Then all your inbound traffic is directly to that single EC2 Instance.
The biggest problem with this model is that if that your Server fails for any reason (whether hardware, or software), then your application will be down and unavailable to your users.
Other examples can be like let’s say you performed a system update, deployed code, or perform any task that makes your server inaccessible, then basically you will end up shutting down your entire website until your Server is up and running again.
Another reason why a Single Server Model is bad is let’s say if you experienced a spike in your traffic and your server is no longer able to handle the workload, then your application will also be inaccessible.
To address those problems, this is where we use AWS Elastic Load Balancing and AWS Autoscaling groups so that all your inbound traffic, is directed to your Load Balancer, then from there to multiple EC2 instances.
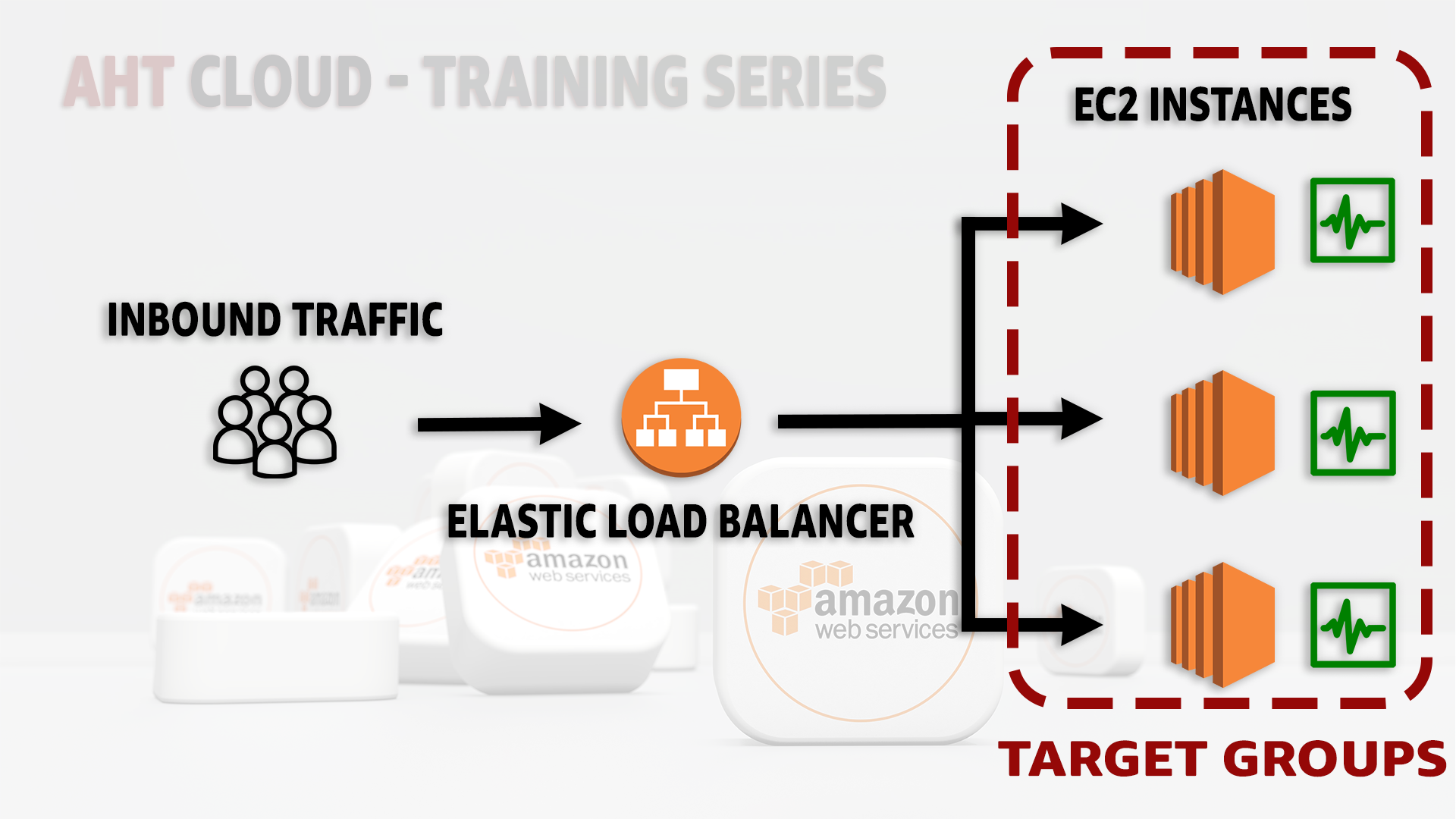
AWS Autoscaling groups will allow us to control the number of EC2 instance and auto scale as traffic increases per our configuration.
To give you a quick summary:
-
Load balancers are used to route your web traffic between two or more servers.
-
EC2 Auto Scaling
What is AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)?
Elastic Load Balancing is commonly referred to as an ELB is a service from Amazon Web Services that automatically routes inbound traffic across multiple targets per your configuration.
These targets could be a set of EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, a range of IP addresses, or even containers.
The targets defined within the ELB could be inside different availability zones (AZs) or within a single Available Zone.
The traffic is distributed based on the target’s health so that all incoming traffic is directed to a healthy instance. if one EC2 instance fails (unhealthy), Elastic Load Balancing automatically routes incoming traffic to the remaining running healthy EC2 instances. If the instance is restored (healthy), Elastic Load Balancing restores incoming traffic to that instance.
There are 4 different types of AWS Elastic Load Balancers:
-
Application Load Balancer – Allows you to route traffic to different ports on the same EC2 Instance. For example, redirect traffic from http to https.
-
Network Load balancer – Used for extreme performance and low latency applications. Allows you to route traffic to targets within your VPC. It Used to load balance network and transport protocols (layer 4 TCP, UDP)
-
Gateway Load Balancer – Allows you to easily deploy, scale and manage virtual appliances such as firewalls, intrusion detection and other systems.
-
Classic Load Balancer – used if your application is built within the EC2 Classic Network.
How Elastic Load Balancing Works?
The main function for Load balancers is to accept in bound traffic and to route it to registered targets that you specified. Registered targets can be one or more EC2 Instances.
Your load balancer is configured to accept incoming traffic by specifying one or more listeners with a protocol and port number.
For example, you can listen to HTTP or HTTPS requests on ports 80 or 443. Then depending on how you configure your Load Balancer, the traffic will be directed accordingly.
Its also worth mentioning that the Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer, and the Gateway Load balancer all allow you to register targets in target groups and route traffic to target group.
For the classic load balancer, you had to register instances with the load balancer.
The classic Load Balancer is deprecated.
Elastic Load Balancers Internet-facing vs Internal
When you create a load balancer, you will have to select one of 2 schemes available for your load balancer: internet -facing and Internal load balancers.
The internet-facing load balancer has both a public IP address and a private IP address.
The internal-facing load balancer has only private IP address.
If your using a load balancer to route traffic for your website application where your traffic are your users, then you will need to use the internet-facing load balancer.
The internal load balancer routes traffic your EC2 instances in private subnet. The clients must have explicit access to the private subnet.
What is AWS EC2 Auto Scaling?
EC2 Auto Scaling is a service from Amazon Web Services.
EC2 Auto Scaling helps you manage your application availability by allowing you to automatically add or remove EC2 instances according to conditions that you define.
You can use it to scale up or scale down depending on how you configure it. This helps you ensure that you have the correct number of instances available to handle your application load.
Auto Scaling groups are a basically collection of EC2 Instances that are created per your configuration.
You can use multiple EC2 instances to host your website and automatically increase, decrease, scale and descale your instances to handle the load.
You can specify the minimum and maximum number of instances in each Auto Scaling Group and EC2 Auto Scaling will ensure that your group never goes above or below your specified values.
You can also set your desired capacity and EC2 Auto Scaling will ensure you have that number of instances running.
If you specify scaling policies, then EC2 Auto Scaling can launch or terminate instances on demand as your application load increases or decreases per your configuration.






















